You've probably heard about omega-3s before but may not fully grasp why they play a vital role in your daily well-being. This article, penned by our registered dietitians, aims to demystify this term and shed light on its impact on your dietary intake and overall wellness.
1. What Are Omega-3s?
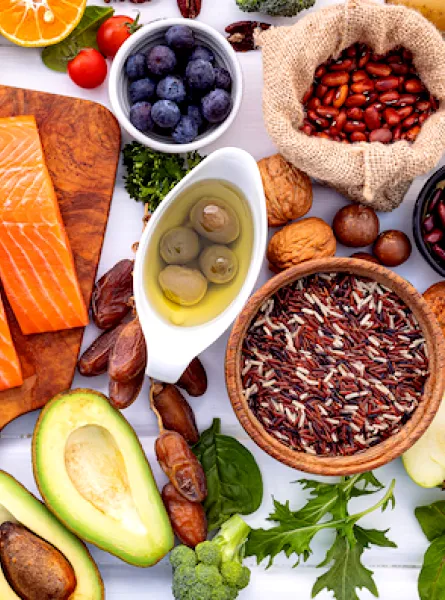
Omega-3 fatty acids are a family of essential lipids, meaning the body can't produce them on its own. They are primarily found in specific food sources, including fatty fish, vegetable oils, nuts, and some seeds. These fatty acids play a critical role in brain function, maintaining cardiovascular health, and preventing chronic diseases.
2. The Benefits of Omega-3s
- Brain Health: Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for brain development and functioning. They may also help prevent Alzheimer's disease and mood disorders such as depression.
- Cardiovascular Health: These fatty acids can reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases by lowering levels of triglycerides in the blood and improving blood pressure.
- Inflammation Reduction: Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties that can help combat various chronic diseases.
3. A Closer Look at EPA and DHA
It's essential to note that omega-3s can be classified into different sub-categories of polyunsaturated fatty acids, namely EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). Both types of omega-3 have their specific health benefits. EPA is known for its anti-inflammatory properties, while DHA is crucial for optimal brain development and functioning. These kinds of omega-3 are mainly found in marine sources like fatty fish and seafood. For those avoiding animal products, marine microalgae can also be a viable source.
4. Where to Find Omega-3s?
From Seafood
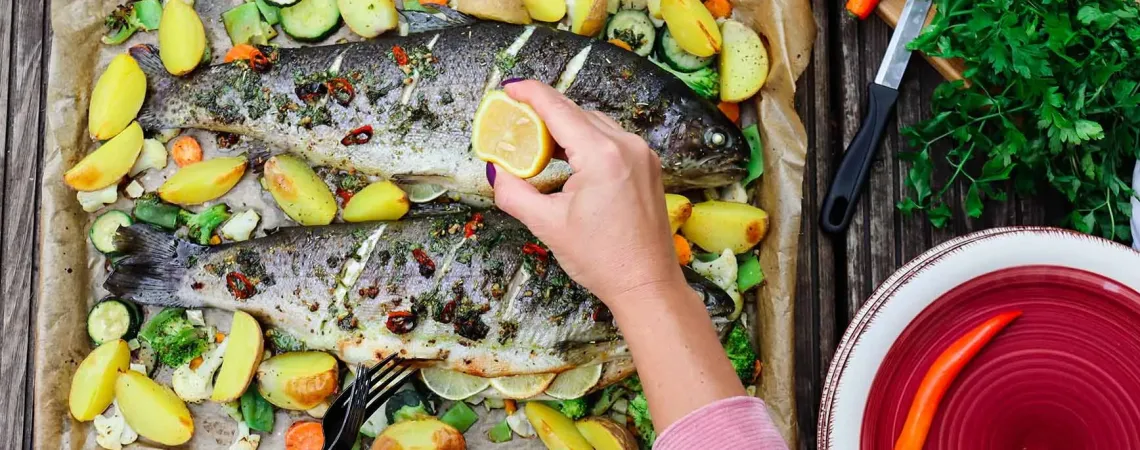
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, herring, anchovies, sardines, caviar, clams, cod, and pollock are excellent sources of omega-3s. If you're not a fan of fish, fish oil or algae-based supplements are good alternatives. Shellfish like mussels and oysters are also sources of this polyunsaturated fatty acid.
From Plants
Flaxseeds, walnuts, pecans, chia seeds, edamame, tofu, and soybeans are other foods rich in omega-3s. Flaxseed oil and canola oil are also good options.
5. Tips to Incorporate Omega-3s into Your Dietary Habits
Eating a balanced diet doesn't mean you need to follow a strict regimen. Just pay attention to what goes on your plate. Here are some suggestions:
- Sprinkle chia seeds on your yogurt or smoothie.
- Make a homemade salad dressing with flaxseed oil.
- Add walnuts to your salads.
- Enjoy salmon as tartare, sushi, or grilled.
- Incorporate anchovies into your pizzas or Niçoise salads.
- Use canola oil for your stir-fries.
- Add ground flaxseeds to your homemade pastries or crackers.
- Opt for a snack mix made of roasted soybeans and nuts.
- Try canned mackerel on crackers for a quick meal.
- Prepare a pollock salad for your sandwiches.
6. Wrapping Up on Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids are not just a health trend; they are an essential component of a balanced diet. They offer undeniable benefits for the brain, heart, and immune system. As registered dietitians, we encourage you to incorporate these valuable nutrients into your daily diet.
Book an Appointment Today
Interested in learning more about how to integrate omega-3s into your diet? Don't hesitate to book an appointment with a registered dietitian for personalized guidance.